Each strand of hair is a protein fiber that grows from a follicle which can be found in the dermis, or skin. In this article, we’re going to go over the structure of hair, how it grows, and the different types that exist in humans.
Hair Structure
Hair fibers have a structure made up of several layers. Each hair is made up of three elements: the medulla, cortex, and cuticle. To put it simply, the innermost layer is the medulla, the middle layer is the cortex, and the outer layer is the cuticle.
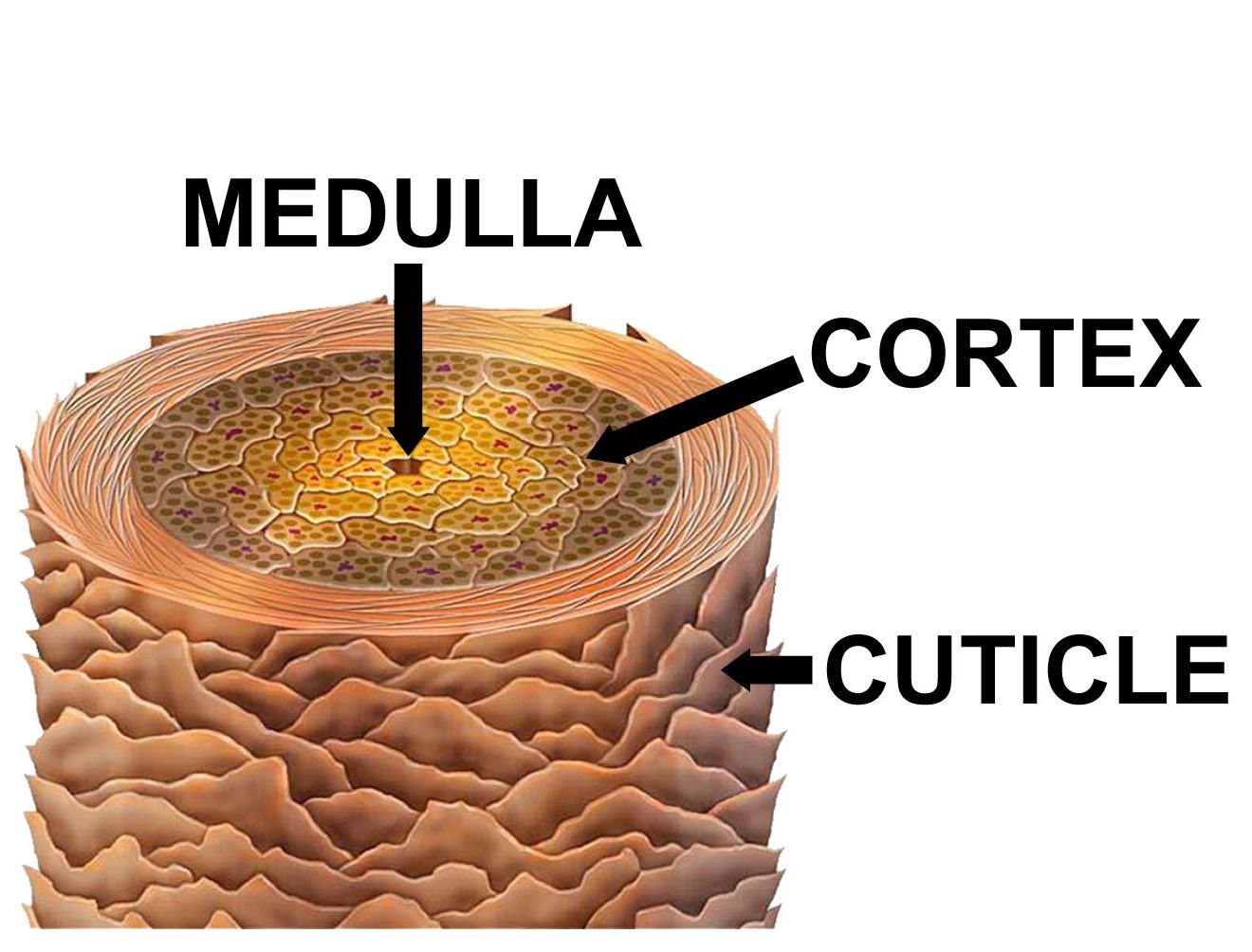
As we said, the outer part of the hair is the cuticle. This consists of thin, flat cells that overlap one another like fish scales. These scales can be several layers thick, which is why the cuticle is responsible for the hair’s flexibility. The cuticle is transparent, allowing the color of the cortex to be visible.
After the cuticle comes the cortex, which contains keratin and melanin in rod-like cells. This is a highly structured and organized layer which is responsible for the hair’s mechanical strength and water uptake. The main bulk of the cortex is long fibers that are twisted together like a rope. The cortex contains melanin, which colors the fiber. This color is based on the number, distribution, and type of melanin granules. For that reason, we can say that the cortex determines the color of the hair.
There are two kinds of pigments in the cortex:
- Eumelanin (which creates brown and black colors).
- Pheomelanin (which creates yellow and red colors).
Finally, the middle part of the hair is the medulla. This is the soft area at the center of the strand.
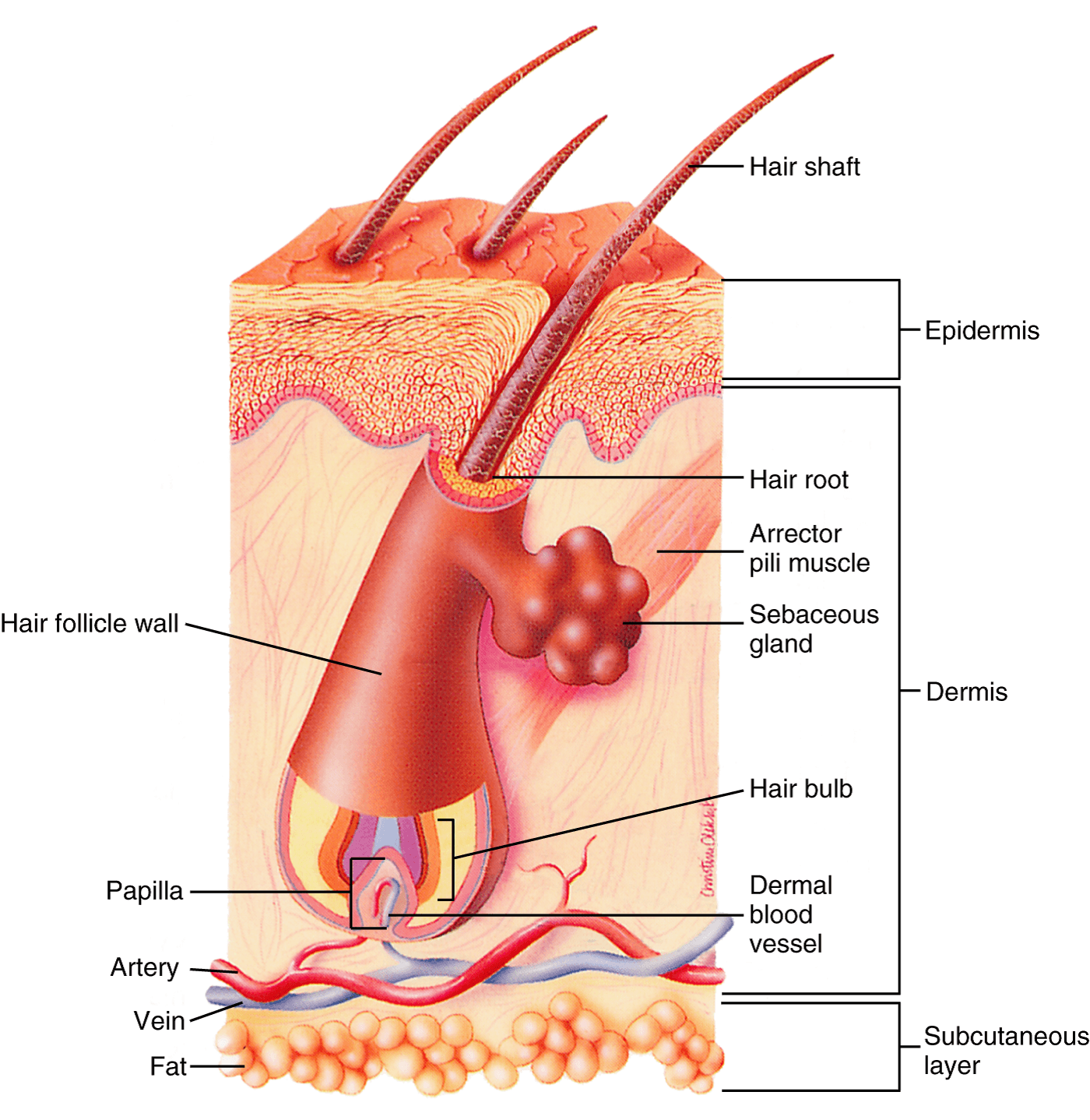
The human head has hundreds of thousands of follicles, which are the pore-like structures within the scalp. The hair begins to grow in the hair follicle from the papilla. This is the only living part of the hair. The hair that is visible on the surface has no biochemical activity and is therefore considered to be dead.
So, hair is mostly made up of dead cells. As the new cells grow, the older cells die and are forced through the follicle towards the scalp. These dead cells are compressed to form a protein called keratin. The hair shaft which is seen above the skin is the keratin. We should mention that each hair consists of keratin, water, and a binding agent that holds the keratin and the water together.
The base of the bulb of the hair contains the cells that are responsible for producing the hair shaft. Each hair follicle also includes a sebaceous gland. This gland is responsible for producing the oil that lubricates the hair. The surrounding muscles called arrector pili muscles, are what cause the hair to stand up. These muscles also create goosebumps!
Hair Growth
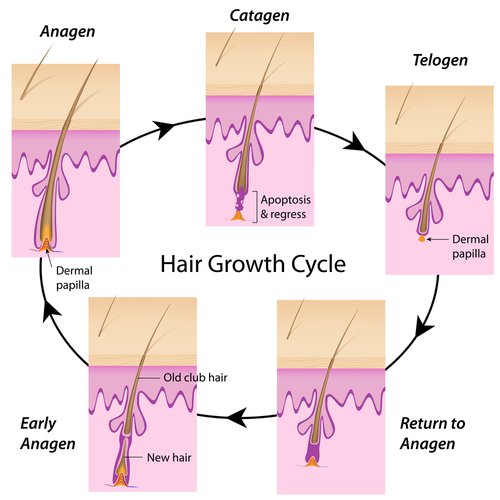
Each hair follicle produces many hairs during the human lifetime. Human hair grows, stops growing, falls out, and then starts to grow again. Of course, there can be several factors that affect this process of renewal. This is what happens when the hair doesn’t grow back (sometimes resulting in baldness). One human hair grows for 1 to 8 years and can grow 12–42 in. (30–106 cm), if it isn’t cut.
In general, there are three stages of hair growth: anagen, catagen, and telogen:
- The anagen stage can last from a month to a few years. This is the main stage of hair growth where the papilla produces most of the hair cells.
- The catagen stage is when the hair stops growing. In this stage, the bulb of the hair shaft separates from the papilla and shrinks upwards.
- The telogen stage is also known as the shedding stage. This is because the follicle stops growing and rests. Then the bulb shrinks and breaks free from the bottom of the follicle, resulting in shed hair. We should mention that during the telogen stage a new hair begins its growth phase, pushing the old one out of the follicle.
Hair Type and Shape
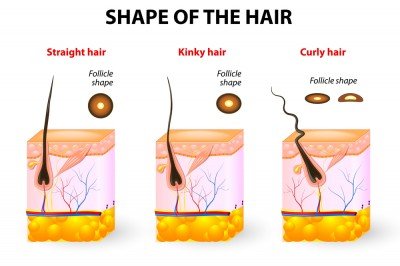
When it comes to the shape of the hair, the shape of the follicle affects the shape of the cortex but it is the shape of the fiber that affects how straight or curly the hair is. For example, people with round hair fibers have straight hair while people with oval or irregularly-shaped fibers will have wavy or curly hair.
Generally, there are three types of hair: African-Caribbean, Asian, and Caucasian (European):
- African-Caribbean hair is usually are very tightly curled and often very dark.
- Asian hair is generally straight and fine but can also be thick and strong. Asian hair ranges from medium brown to very dark.
- Caucasian or European hair can be straight, wavy, or even curly and varies in color from light blond to very dark brown.
Hair Texture
When talking about hair texture, it can be fine, medium, or coarse. The texture of the hair is determined using its circumference and cuticle condition. Fine hair, for example, has a smaller circumference than medium or coarse hair. The diameter of a single human hair varies from 0.017 to 0.18 mm. The texture of hair can vary greatly since it depends on the hair color and racial makeup of the person it comes from.
Hair Density
Finally, hair density is based on the number of hairs on the head. People with fine hair may have more hairs on their head than people with coarse hair. Your hair density depends on several factors, of course. On average, blonde-haired people have 130,000 hairs on their head. Brown-haired and black-haired people have around 110,000 hairs. Red-haired, African-Caribbean and Asian people generally have about 90,000 hairs.